The Ultimate Guide to AI Prompting: How Prompts Work in OpenAI, Claude, and Top AI Systems 2026
What is AI Prompting?
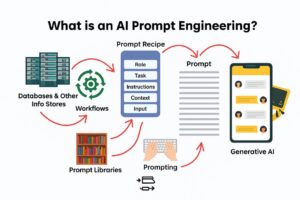
AI prompting is the art and science of crafting input instructions that guide artificial intelligence models to produce desired outputs. A prompt serves as the communication bridge between human intent and AI capability, transforming natural language instructions into actionable tasks for machine learning models.
At its core, prompting is about context setting. When you provide a prompt to an AI system, you’re establishing the framework within which the AI will operate, defining the task parameters, output format, tone, and specific requirements you need.
Why Prompting Matters in 2025
With the rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4, Claude, Gemini, and others, effective prompting has become a crucial skill for:
- Business professionals automating content creation
- Developers integrating AI into applications
- Content creators scaling their output
- Researchers analyzing complex data
- Students enhancing their learning process
How Prompts Work: The Technical Foundation 
The Neural Network Processing Pipeline
When you submit a prompt to an AI system, several sophisticated processes occur:
1. Tokenization The AI breaks down your prompt into tokens (words, subwords, or characters). For example, “Hello world” might become [“Hello”, ” world”] tokens.
2. Embedding Creation Each token is converted into numerical representations (vectors) that capture semantic meaning and relationships between concepts.
3. Attention Mechanisms The AI uses attention layers to understand which parts of your prompt are most relevant to generating each part of the response.
4. Context Window Processing Modern AI systems maintain a context window (ranging from 4K to 200K+ tokens) that allows them to consider the entire conversation history.
5. Probabilistic Generation The AI generates responses by predicting the most likely next tokens based on patterns learned during training.
Understanding Model Architecture Impact
Different AI architectures process prompts differently:
Transformer-Based Models (GPT, Claude, Gemini)
- Excel at understanding context and maintaining coherence
- Process prompts sequentially but can attend to all previous tokens
- Strong performance on complex reasoning tasks
Mixture of Experts Models
- Route different parts of prompts to specialized sub-networks
- More efficient processing for diverse task types
- Better scaling for complex multi-modal prompts
Prompt Engineering Across Major AI Platforms
OpenAI GPT Models (GPT-4, GPT-4 Turbo, GPT-4o)
OpenAI’s models excel with structured, detailed prompts. Key characteristics:
Strengths:
- Superior reasoning capabilities
- Excellent code generation
- Strong mathematical problem-solving
- Consistent output formatting
Optimal Prompting Strategies:
- Use clear role definitions
- Provide step-by-step instructions
- Include specific formatting requirements
- Leverage system messages for consistent behavior
Example OpenAI Prompt Structure:
System: You are an expert data analyst with 10 years of experience.
User: Analyze the following sales data and provide insights:
[Data here]
Please structure your response as:
1. Key findings (3-5 bullet points)
2. Trend analysis
3. Actionable recommendations
4. Risk factors to consider
Anthropic Claude Models
Claude models respond well to conversational, detailed prompts with clear reasoning chains:
Strengths:
- Excellent safety and helpfulness balance
- Strong analytical thinking
- Superior handling of nuanced requests
- Effective at complex reasoning tasks
Optimal Prompting Strategies:
- Use natural, conversational language
- Provide context and reasoning for requests
- Include examples when possible
- Be specific about desired output format
Google Gemini/Bard
Google’s models excel with multimodal prompts and real-time information:
Strengths:
- Strong multimodal capabilities (text, image, video)
- Real-time web access
- Excellent for research and fact-checking
- Strong performance on creative tasks
Optimal Prompting Strategies:
- Leverage multimodal inputs when relevant
- Ask for real-time information
- Use for research-heavy tasks
- Combine multiple media types in prompts
Microsoft Copilot
Integrated with Microsoft ecosystem, optimized for productivity:
Strengths:
- Deep Office 365 integration
- Strong productivity-focused responses
- Excellent for business applications
- Context awareness within Microsoft apps
Optimal Prompting Strategies:
- Reference specific documents or data
- Use for productivity enhancement
- Leverage integration with Office apps
- Focus on business outcomes
Types of AI Prompts and Their Applications
1. Instructional Prompts
Direct commands that specify exactly what you want the AI to do.
Structure: Action verb + specific requirements + context
Example:
Write a professional email to decline a meeting invitation.
The meeting is about quarterly budget reviews, scheduled for Friday at 2 PM.
I need to decline due to a client emergency.
Tone should be apologetic but professional.
Include an offer to review materials offline.
2. Role-Based Prompts
Assign the AI a specific persona or expertise area.
Structure: “You are a [role] with [expertise/background]…”
Example:
You are a senior marketing manager with 15 years of experience in B2B SaaS companies.
You specialize in growth marketing and have successfully scaled multiple companies from Series A to IPO.
Create a comprehensive go-to-market strategy for a new project management tool targeting remote teams of 50-200 employees.
Include pricing strategy, channel partnerships, and a 12-month launch timeline.
3. Few-Shot Learning Prompts
Provide examples to establish patterns and desired output format.
Structure: Example 1 + Example 2 + “Now do this…” + New task
Example:
Here are examples of good product descriptions:
Product: Wireless Headphones
Description: "Experience crystal-clear sound with our premium wireless headphones.
40-hour battery life, noise cancellation, and comfort-fit design make these perfect for work, travel, or relaxation.
Compatible with all Bluetooth devices."
Product: Organic Coffee Beans
Description: "Single-origin Ethiopian beans, ethically sourced and roasted to perfection.
Notes of chocolate and citrus create a complex, smooth flavor profile.
Perfect for pour-over, French press, or espresso brewing methods."
Now write a product description for:
Product: Smart Fitness Tracker
4. Chain-of-Thought Prompts
Guide the AI through step-by-step reasoning processes.
Structure: “Think through this step by step…” + specific reasoning request
Example:
I need to decide whether to expand my online business to international markets.
Think through this step by step:
1. First, analyze the key factors I should consider
2. Then, evaluate the pros and cons of international expansion
3. Consider the risks and mitigation strategies
4. Finally, provide a framework for making this decision
My business: E-commerce platform selling handmade jewelry, currently serving US market with $2M annual revenue, 3-person team.
5. Contextual Prompts
Provide rich background information to inform the AI’s response.
Example:
Context: I'm a freelance graphic designer working with a sustainable fashion startup.
They're launching their first collection next month - organic cotton basics in earth tones.
Their target audience is environmentally conscious millennials and Gen Z consumers who value quality over quantity.
Budget is limited but they want to make a strong first impression.
Task: Design a social media content strategy for their Instagram launch campaign.
Include post types, hashtag strategy, and engagement tactics that align with their sustainable values and resonate with their target audience.
Advanced Prompting Techniques
1. Prompt Chaining
Break complex tasks into sequential prompts, using outputs from one as inputs to the next.
Application: Creating a complete marketing campaign
Prompt 1: "Analyze this target market and identify key pain points: [market description]"
↓
Prompt 2: "Based on these pain points [insert results from Prompt 1], create 5 unique value propositions"
↓
Prompt 3: "Using value proposition #2 [insert selected proposition], write ad copy for Facebook ads"
2. Multi-Modal Prompting
Combine text, images, and other media for richer context.
Example:
[Upload image of a messy desk]
"Analyze this workspace image and provide:
1. Productivity assessment
2. Organization recommendations
3. Suggested improvements for focus and efficiency
4. Budget-friendly solutions under $100"
3. Constraint-Based Prompting
Use limitations to guide creative output.
Example:
Write a compelling product launch email with these constraints:
- Maximum 150 words
- Must include "revolutionary" and "limited-time"
- Cannot use exclamation points
- Must have clear call-to-action
- Tone: professional but enthusiastic
4. Iterative Refinement
Use follow-up prompts to improve outputs.
Example:
Initial: "Write a blog post about remote work productivity"
↓
Refinement 1: "Make this more actionable with specific tips"
↓
Refinement 2: "Add statistics to support the main points"
↓
Refinement 3: "Reorganize with subheadings for better readability"
5. Meta-Prompting
Ask the AI to improve or create prompts.
Example:
"I want to create prompts that help generate high-converting email subject lines for e-commerce.
Create 3 different prompt templates that would produce diverse, effective subject lines.
Each template should target different psychological triggers (urgency, curiosity, benefit-focused)."
Real-World Prompt Examples
Business Applications
1. Meeting Summary Generation
Transform this meeting transcript into an executive summary:
[Transcript content]
Format:
- Key decisions made
- Action items with owners and deadlines
- Open questions requiring follow-up
- Next meeting date and agenda items
Audience: C-level executives who weren't present
Length: Maximum 400 words
2. Competitive Analysis
You are a strategic analyst at a consulting firm.
Conduct a competitive analysis comparing our SaaS product to three main competitors.
Our product: [Description]
Competitors: [List with brief descriptions]
Analysis framework:
1. Feature comparison matrix
2. Pricing strategy analysis
3. Market positioning assessment
4. Strengths/weaknesses evaluation
5. Strategic recommendations
Present findings in a format suitable for board presentation.
Content Creation
1. Blog Post Optimization
Optimize this blog post for SEO and engagement:
[Original blog post content]
Requirements:
- Target keyword: "digital marketing automation"
- Add compelling subheadings
- Include 2-3 relevant statistics
- Create engaging introduction and conclusion
- Suggest internal linking opportunities
- Maintain original tone and expertise level
2. Social Media Content Calendar
Create a 30-day social media content calendar for LinkedIn:
Business: B2B consulting firm specializing in digital transformation
Audience: CTOs, IT Directors, Digital Leaders at Fortune 500 companies
Goals: Thought leadership, lead generation, community building
Content mix:
- 40% educational content
- 30% industry insights
- 20% company updates
- 10% engagement posts
Include: Post topics, optimal posting times, hashtag suggestions, and engagement strategies.
Technical Applications
1. Code Review and Optimization
Review this Python function and provide optimization recommendations:
[Code snippet]
Focus areas:
1. Performance improvements
2. Code readability
3. Error handling
4. Best practices compliance
5. Security considerations
Provide before/after examples for each suggested improvement.
2. API Documentation Creation
Create comprehensive API documentation for this endpoint:
Endpoint: POST /api/v1/users
Purpose: Create new user account
Include:
- Clear description
- Parameters (required/optional)
- Request/response examples
- Error codes and messages
- Authentication requirements
- Rate limiting information
- SDK examples in Python and JavaScript
Educational Applications
1. Lesson Plan Generation
Create a comprehensive lesson plan:
Subject: High school chemistry
Topic: Chemical bonding and molecular structure
Duration: 90 minutes (block schedule)
Class size: 25 students
Available resources: Lab equipment, digital projector, molecular model kits
Include:
- Learning objectives aligned with state standards
- Pre-assessment activity
- Step-by-step lesson activities
- Hands-on laboratory component
- Assessment rubric
- Homework assignment
- Differentiation strategies for diverse learners
Common Prompting Mistakes to Avoid
1. Vague or Ambiguous Instructions
Poor Example: “Write something about marketing”
Better Example: “Write a 1000-word guide explaining content marketing strategies for small businesses, including 5 specific tactics with implementation steps.”
2. Overloading with Information
Poor Example: “Here’s everything about our company [3000 words of context]. Now write a tweet.”
Better Example: “Our company sells eco-friendly home products to environmentally conscious consumers. Write a tweet announcing our new bamboo kitchenware line that emphasizes sustainability and quality.”
3. Lack of Format Specification
Poor Example: “Analyze this data and tell me what you find.”
Better Example: “Analyze this sales data and present your findings as: 1) Executive summary (2-3 sentences), 2) Key trends (bullet points), 3) Recommendations (numbered list), 4) Next steps (timeline format).”
4. Ignoring Context and Audience
Poor Example: “Explain blockchain technology.”
Better Example: “Explain blockchain technology to a group of retail business owners who are considering accepting cryptocurrency payments. Focus on practical benefits and address common security concerns.”
5. Single-Shot Complex Tasks
Poor Example: “Create a complete marketing strategy for my new app including market research, competitor analysis, pricing, and launch plan.”
Better Example: Break into sequential prompts:
- Market research analysis
- Competitor evaluation
- Pricing strategy development
- Launch plan creation
Measuring Prompt Effectiveness
Key Performance Indicators
1. Output Relevance
- Does the response address all aspects of your prompt?
- Is the information accurate and up-to-date?
- Does it match your intended use case?
2. Quality Metrics
- Clarity and readability
- Depth of analysis
- Actionability of recommendations
- Professional tone and formatting
3. Efficiency Measures
- Time saved compared to manual creation
- Number of iterations needed for satisfactory output
- Consistency across multiple similar prompts
A/B Testing Prompts
Version A (Basic): “Write a product description for our new smartwatch.”
Version B (Detailed): “Write a compelling 150-word product description for our new fitness-focused smartwatch. Target audience: active professionals aged 25-45. Highlight unique features: 14-day battery life, health monitoring, and seamless phone integration. Tone: enthusiastic but professional. Include a clear call-to-action.”
Compare outputs for conversion rates, engagement, and user feedback.
The Future of AI Prompting 
Emerging Trends
1. Multimodal Integration
- Voice + text + image prompting
- Real-time visual context understanding
- Interactive prompt refinement
2. Automated Prompt Optimization
- AI systems that improve their own prompts
- Dynamic prompt adaptation based on user feedback
- Personalized prompting styles
3. Domain-Specific Prompt Libraries
- Industry-specialized prompt templates
- Role-based prompt collections
- Task-specific optimization frameworks
4. Collaborative Prompting
- Team-based prompt development
- Shared prompt repositories
- Version control for prompt engineering
Preparing for Advanced AI Systems
As AI capabilities continue to expand, effective prompting will become even more crucial:
Skills to Develop:
- Systems thinking for complex prompt chains
- Understanding of AI limitations and biases
- Creativity in prompt design and application
- Analytical skills for measuring prompt effectiveness
Best Practices Evolution:
- Increased focus on ethical AI use
- Privacy-conscious prompt design
- Transparency in AI-assisted work
- Continuous learning and adaptation
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of AI Prompting
Effective AI prompting is both an art and a science that combines clear communication, strategic thinking, and technical understanding. As AI systems become more sophisticated, the ability to craft precise, contextual, and results-oriented prompts becomes increasingly valuable.
The key to prompt mastery lies in:
Understanding your AI platform’s strengths and characteristics Each AI system has unique capabilities and responds differently to various prompting approaches.
Practicing iterative refinement Great prompts are rarely perfect on the first try. Develop a habit of testing, measuring, and improving your prompts.
Building a systematic approach Develop templates and frameworks for common tasks while remaining flexible for unique challenges.
Staying current with AI developments The field evolves rapidly, and new techniques and best practices emerge regularly.
Focusing on clear communication At its core, prompting is about communicating effectively with an AI system to achieve your desired outcomes.
By mastering these principles and continuously practicing with real-world applications, you’ll be well-equipped to leverage AI systems effectively across any domain or industry. The future belongs to those who can effectively collaborate with AI, and that collaboration starts with excellent prompting skills.
Ready to take your AI prompting skills to the next level? Start implementing these techniques today and watch your AI interactions become more productive, precise, and powerful.